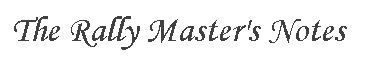
Flow Charts
PART ONE
Rally masters with an engineering background sometimes present the route as a process control chart, which looks bewildering to most of us non-scientific types. While you must stay alert, these type of instructions are not as difficult as they initially appear.
A flow chart is based on a series of questions to which you must answer yes or no; there are no 'maybes'. In the example below there are boxes which contain either questions or instructions. There are circles with the possible answers yes or no. These shapes are connected by arrows which shows you the logic "flow". There are no distances given for turns; you must travel to the next intersection and answer the next question. However, you must also know how far you have travelled from the start of the section as your cummulative distance may be required to answer a question. You may go in circles on the chart, using an instruction multiple times. Again, stay alert always know where you are on the chart and what the next question to be answered is! Time to practise - using the partial flow chart example given, follow the route through the chart.

- Are you on a paved road? (No) Can you turn right? (No) Straight ahead.
- Are you on a paved road? (No) Can you turn right? (No) Straight ahead.
- Are you on a paved road? (Yes) Can you go straight ahead? (Yes) Can you bear left on Concession 3? (No) Straight ahead.
- Are you on a paved road? (No) Can you turn right? (Yes) Have you travelled more than 15.7 Km? (No) Straight ahead.
- Are you on a paved road? (Yes) Can you go straight ahead? (Yes) Can you bear left on Concession 3? (Yes) Bear left.
PART TWO
Here are 2 more examples of flowcharts. Remember, flowchart decisions are binary; either an instruction is clearly right or it is clearly wrong!
Tulip Flowchart
Starting at the top of the chart, find the tulip that matches the intersection that you are currently at. The first time that you use this tulip, execute all of the corresponding instructions in column 1, until you complete the column. The next time you use the tulip, complete column 2, etc. Once a column is complete, drive to the next intersection and find the tulip that matches and again complete a column.
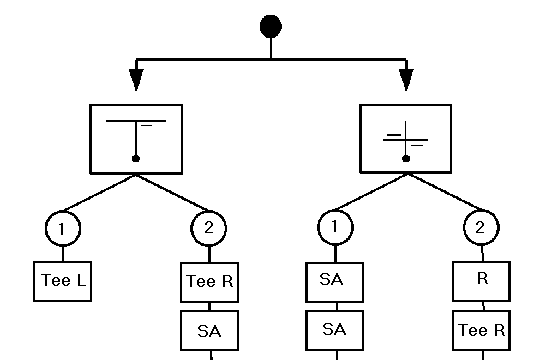
Non-accumulative Distance Flowchart
At each stop sign, including Start of Section, you will begin in the box marked stop and proceed along one of the lines, performing the first action which the route will allow. Each box contains an instruction and the non-accumulative distance from the previous intersection. Continue "flowing" downward, either diagonally or straight, obeying the instructions given. After executing an instruction at a stop sign, begin again from the box marked stop.
| Back To Rally Master's Index |
Last Updated: 2002-01-14
Copyright © 2001 Gail L. Walker, reproduction forbidden without written authorization.